Session, Cookie, JWT, Token, SSO, and OAuth 2.0
Session, Cookie, JWT, Token, SSO, and OAuth 2.0 Explained in One Diagram
Diagram
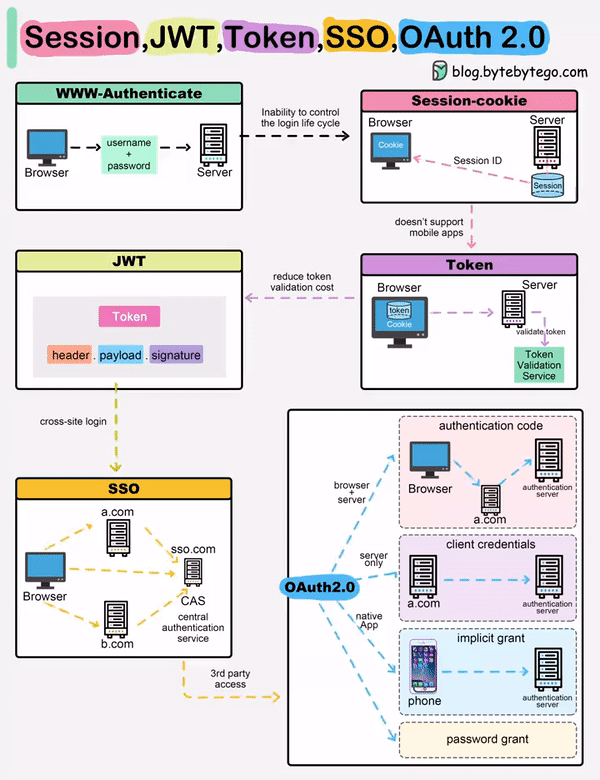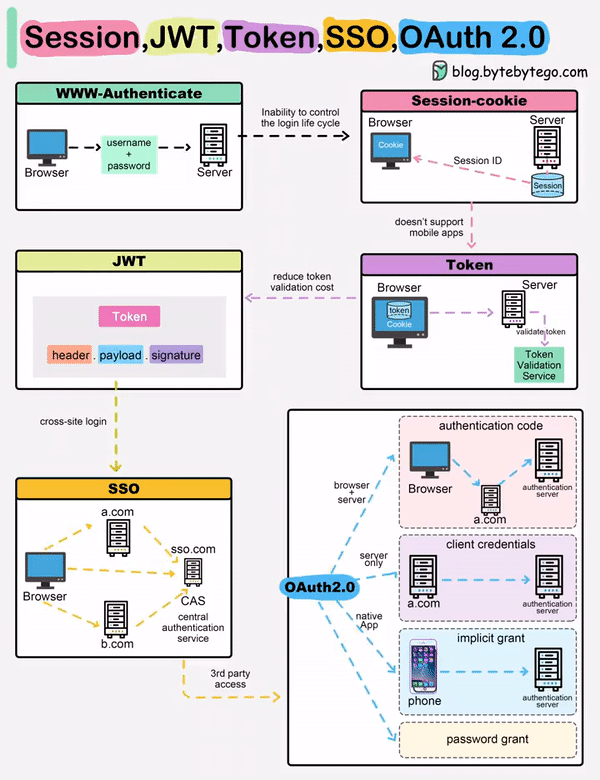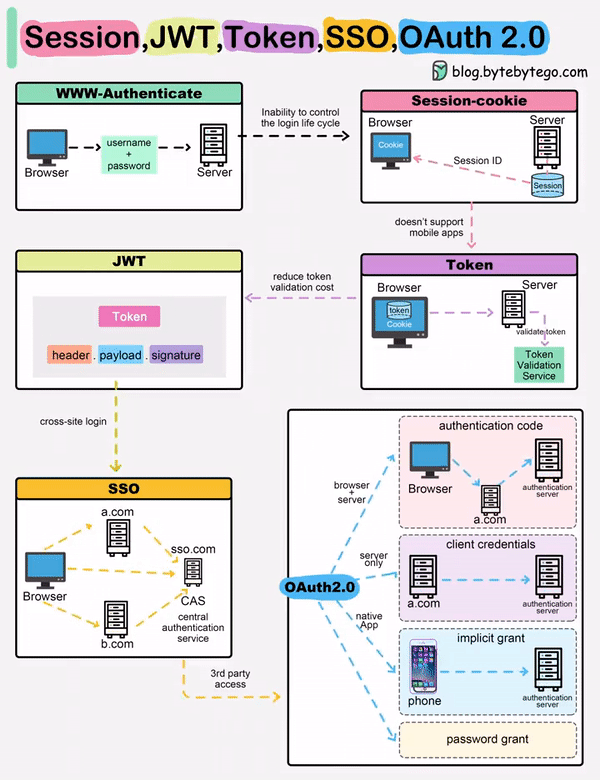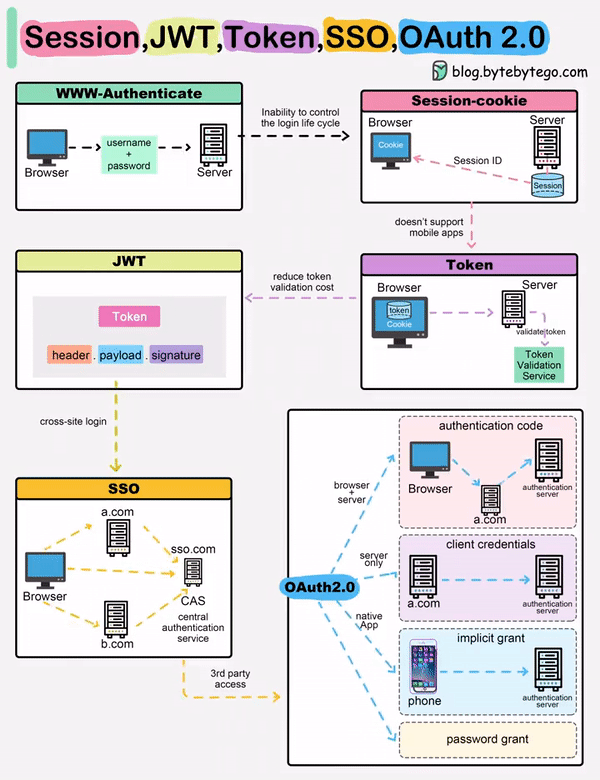
When you login to a website, your identity needs to be managed. Here is how different solutions work:
Session - The server stores your identity and gives the browser a session ID cookie. This allows the server to track login state. But cookies don't work well across devices.
Token - Your identity is encoded into a token sent to the browser. The browser sends this token on future requests for authentication. No server session storage is required. But tokens need encryption/decryption.
JWT - JSON Web Tokens standardize identity tokens using digital signatures for trust. The signature is contained in the token so no server session is needed.
SSO - Single Sign On uses a central authentication service. This allows a single login to work across multiple sites.
OAuth2 - Allows limited access to your data on one site by another site, without giving away passwords.
QR Code - Encodes a random token into a QR code for mobile login. Scanning the code logs you in without typing a password.
 Beijing
Ally-World
Beijing
Ally-World